Introduction
Mercanet is a secure multi-channel e-commerce payment solution that complies with the PCI DSS standard. It allows you to accept and manage payment transactions by taking into account business rules related to your activity (payment upon shipping, deferred payment, recurring payment, payment in instalments, etc.).
The purpose of this document is to explain the implementation steps of the solution up to live operations.
Who does this document target?
This document is intended for merchants wishing to subscribe to the Mercanet offer and integrate payment as part of their mobile application. The In-App connector is based on JSON exchanges via the REST protocol, in machine-to-machine mode.
It is an implementation guide for your technical team.
To get an overview of the Mercanet solution, we advise you to consult the following documents:
Prerequisites
Knowledge of standards related to web programming languages used today, such as Java, PHP or .Net, is necessary to develop a client that can connect to the In-App gateway.
Furthermore, knowledge of standards related to mobile programming languages used today is necessary to integrate our SDK to your Android and iOS mobile application.
Secret key management
Upon your subscription, BNP Paribas provides a secret key on the Mercanet Téléchargement extranet that will allow you to secure exchanges between your website and the Mercanet server.
You are responsible for looking after this key and should take all measures to:
- restrict access to the key
- safeguard it by encrypting it
- never copy it onto a non-secure disc or device
- never send it (via e-mail or regular mail) in a non-secure method
A secret key compromised (and used by a malicious third party) might disrupt the regular operation of your shop and might in particular generate unauthorised sales or cash transactions (e.g. refunds).
The very same secret key is used on the various Paypage, Office (M2M), In-App and Walletpage connectors.
keyVersion field with the new
version, otherwise you will get an answer code 34 (suspected
fraud).Complying with PCI-DSS
Worldline has lowered PCI-DSS constraints on your side because encrypted card data passes between your mobile applications and the Mercanet server.
Indeed, card data never flows through your server and this must never be the case.
Therefore, your application does not have to comply with the PCI-DSS standard; it simply has to comply with the PCI-DSS best practices described at this address:
https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/document_library?association=PA-DSS
Understanding In-App
The general principle of how In-App works is the following:
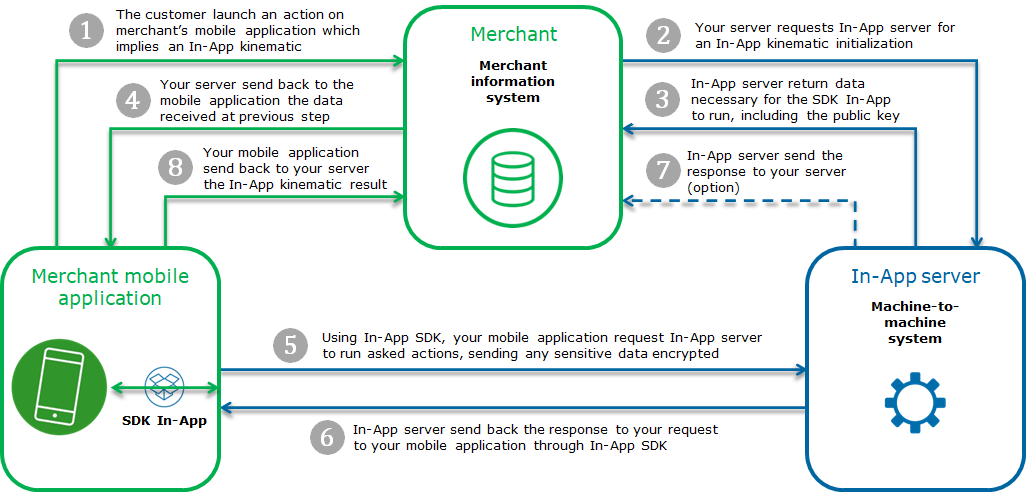
Getting-started with In-App in 6 steps
Step 1: registering the shop
In order to register your shop as live, you are required to complete the registration form sent by BNP Paribas and send the form back to the latter.
When filling in the form, you must appoint an administrator contact and a technician contact so that BNP Paribas can send you the information needed to launch your shop.
BNP Paribas will then register your shop and e-mail you your merchant ID, together with your IDs and passwords for Merchant Extranet (to retrieve the secret key and perform cash management).
Registering the shop is not needed to start integrating the connector and testing the connection on the customer test environment. It is possible to defer requesting shop registration until you perform live operation tests.
Step 2: initializing a In-App kinematic
As mentioned above, the first step of a In-App kinematic consists in initializing this kinematic. This initialization is a call to a REST (JSON) web service located on the Mercanet payment platform.
A request is made up of generic fields and container fields.
A container is a structure used to functionally group data.
If the field is a container, this specification is indicated in the comment column which refers you to the dedicated chapter detailing the contents of all the fields of this type.
All of the necessary fields must be provided for each request.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>415 Unsupported Media Type</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Unsupported Media Type</h1>
<p>The supplied request data is not in a format
acceptable for processing by this resource.</p>
</body>
</html>Request syntax
The request is structured in line with the JSON format:
{“<nom du champ>” : ”<nom de la valeur>”, “<nom du champ>” : “<nom de la valeur>”, “nom du champ” : “Nom de la valeur” etc., “seal” : “valeur de seal”}Sample payment request with an amount of 10 euros:
{"amount" : "1000","currencyCode" : "978","interfaceVersion" : "IR_MB_2.38","keyVersion" :
"1","merchantId" : "012345678911111","paymentMeanBrand" : "VISA","paymentPattern" :
"ONE_SHOT","sdkOperationName" : "CARDORDER","transactionReference" : "STHTSH4418152014","seal" :
"05f6b5cc0b2a31eb3a976f060a3824874cc7bf01c081f17956f125f586eb27ba"}The syntax used to create a JSON list complies with the standard. Here is a summary of this structure for the two main list types: simple field lists (e.g. character strings) and object lists.
A field can have several values:
…,"nom du champ" : ["valeur1","valeur2"],…Sample paymentMeanBrandList field with VISA and MASTERCARD as values:
…,"paymentMeanBrandList" : ["VISA","MASTERCARD"],…If a field contains a list of complex objects, its representation is structured using the following format:
…,“nom du champ” : [{“nom du sous-champ1”:”valeur1”,“nom du sous-champ2”:”valeur2”},{“nom du souschamp1”:”valeur3”, “nom du sous-champ2”:”valeur4”}],…Sample payment request with a list of complex objects for the shoppingCartDetail field, containing two products, apple and mango:
{"amount" : "1000","currencyCode" : "978","interfaceVersion" : "IR_MB_2.38","keyVersion" :
"1","merchantId" : "012345678911111","paymentMeanBrand" : "VISA","paymentPattern" :
"ONE_SHOT","sdkOperationName" : "CARDORDER","shoppingCartDetail" : {"shoppingCartItemList" : [{"productCode" :
"123","productName" : "apple"},{"productCode" : "456","productName" : "mango"}],"shoppingCartTotalAmount" :
"1000"},"transactionReference" : "6549854FCEX12867","seal" :
"17cb94b79102b492eccd335cb8e5633e243f12ce116a496b45c93d7b6908bb0b"}Request fields presence
Some fields of the payment request are required:
- Only when using certain means of payment. Please read the dedicated means of payment guide to know the mandatory fields.
- Depending on your shop configuration. Please read the Functionality set-up guide to find out the mandatory fields.
- Only in certain use cases (e.g. recurring payment). Please read the Functionality set-up guide to know the mandatory fields.
Those fields are marked as "conditional".
Securing the request
The request includes the transaction parameters and is sent by your server. Theoretically, a third party can intercept the request and modify its content before the data reaches the payment server.
Therefore it is necessary to strengthen security so as to ensure the integrity of the parameters of the transaction sent. The Mercanet solution meets this challenge by exchanging signatures. An effective signature control comprises two elements:
- The integrity of the request and response messages (and therefore the absence of modifications during the exchange).
- The issuer and recipient authentication, as they share the same secret key.
How to secure the request
The request is secured by calculating the hash value in line with the transaction parameters. Then, the secret key is added to it. All character strings are converted to UTF-8 before being hashed.
The hashing algorithm generates an irreversible result. When such a message is received, the recipient needs to recalculate the hash value and compare it with the one received. Any difference indicates that the data exchanged was falsified, or that the recipient and the issuer do not share the same secret key.
The result must be sent in hexadecimal format in the data element named Seal.
Calculating the Seal data element
HMAC-SHA algorithm
The value of the Seal data element is computed as follows:
- Concatenation of data field values in the alphabetical order of
field names (in accordance with ASCII character codes), without
integrating the keyVersion and sealAlgorithm fields.
Giving the field data, mentioned in the examples below.
- as an example, a field that would be named authorMessageReference must be positioned before another field named authorisationId
- Obtaining the UTF-8 encoding of the data from the previous result
- HMAC with SHA256 encryption of bytes obtained with the secret key
This procedure can be summarised as follows:
HMAC-SHA256( UTF-8(sortedDataValues), UTF-8(secretKey))For the seal to be computed with the SHA-256 algorithm,
the input parameters of the request must include the sealAlgorithm field populated with the
following value: “SHA-256”.
Hmac Sha256 sample code
- Sample Hmac Sha256 encoding in Php 5
<?php … // Seal computation thanks to hash sorted data hash with merchant key $data_to_send= utf8_encode($data) $seal=hash_hmac('sha256', $data_to_send, $secretKey); … … ?>data_to_send and secretKey must use a UTF-8 character set. Please refer to the utf8_encode function for the conversion of ISO-8859-1 characters in UTF-8.
- Sample Hmac Sha256 encoding in Java
import java.security.InvalidKeyException; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import javax.crypto.Mac; import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec; public class ExampleHMACSHA256 { /** * table to convert a nibble to a hex char. */ static final char[] hexChar = { '0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' , '6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f'}; /** * Fast convert a byte array to a hex string * with possible leading zero. * @param b array of bytes to convert to string * @return hex representation, two chars per byte. */ public static String encodeHexString ( byte[] b ) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer( b.length * 2 ); for ( int i=0; i<b.length; i++ ) { // look up high nibble char sb.append( hexChar [( b[i] & 0xf0 ) >>> 4] ); // look up low nibble char sb.append( hexChar [b[i] & 0x0f] ); } return sb.toString(); } /** * Computes the seal * @param Data the parameters to cipher * @param secretKey the secret key to append to the parameters * @return hex representation of the seal, two chars per byte. */ public static String computeSeal(String data, String secretKey) throws Exception { Mac hmacSHA256 = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256"); SecretKeySpec keySpec = new SecretKeySpec(secretKey.getBytes(), "HmacSHA256"); hmacSHA256.init(keySpec); return encodeHexString(hmacSHA256.doFinal(data.getBytes())); } /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { try { System.out.println (computeSeal("parameters", "key")); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } - Sample Hmac Sha256 encoding in .net
(Carried out using a simple form called "Form1" containing two text fields to enter data and txtSecretKey, and another field to display lblHEX).
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Text; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Security.Cryptography; namespace ExampleDotNET { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void cmdGO_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { String sChaine = data.Text; UTF8Encoding utf8 = new UTF8Encoding(); Byte[] encodedBytes = utf8.GetBytes(sChaine); byte[] shaResult; HMAC hmac = new HMAC.Create("HMACSHA256"); var key = "YourSecretKey"; hmac.Key = utf8.GetBytes(key); hmac.Initialize(); shaResult = hmac.ComputeHash(encodedBytes); lblHEX.Text = ByteArrayToHEX(shaResult); } private string ByteArrayToHEX(byte[] ba) { StringBuilder hex = new StringBuilder(ba.Length * 2); foreach (byte b in ba) hex.AppendFormat("{0:x2}", b); return hex.ToString(); } } }
Seal calculation validation
Once you have set up your seal calculation, here is a sample request to help you verify that you find the correct seal:
{
"amount" : "2500",
"automaticResponseUrl" : "https://automatic-response-url.fr/",
"captureDay" : "0",
"captureMode" : "AUTHOR_CAPTURE",
"currencyCode" : "978",
"interfaceVersion" : "IR_MB_2.38",
"keyVersion" : "1",
"merchantId" : "011223344550000",
"sdkOperationName" : "CARDORDER",
"sdkVersion" : "SDK100",
"transactionReference" : "TREFEXA2021",
"seal" : "c4372c03a0d678fcf5a401d6a7d8625785580d07257208b8c0dc098e0109963a"
}For the above request, the concatenated string you must obtain is:
2500https://automatic-response-url.fr/0AUTHOR_CAPTURE978IR_MB_2.38011223344550000CARDORDERSDK100TREFEXA2021With a HMAC-SHA-256 hash algorithm and the following secret key:
secret123The expected seal is:
c4372c03a0d678fcf5a401d6a7d8625785580d07257208b8c0dc098e0109963aInitializing a payment kinematic
With In-App connector, you are able to launch
several kind of payment kinematic according to sdkOperationName
field, filled in orderInitialize service request:
- Card payment kinematic without holder authentication (
sdkOperationName=CARDORDER) - Card payment kinematic with holder authentication (
sdkOperationName=THREEDSECUREANDORDER) - Wallet payment kinematic without holder authentication (
sdkOperationName=WALLETORDER) - Wallet payment kinematic with holder authentication (
sdkOperationName=THREEDSECUREANDWALLETORDER) - Externalized payment kinematic on a payment provider (
sdkOperationName=PAYMENTPROVIDERORDER)
These kinematics are described hereafter.
Card payment kinematic without holder authentication
A card payment kinematic without holder authentication with In-App is done in 2 steps:
- Initialize the payment kinematic on Mercanet server
through orderInitialize service (with
sdkOperationName=CARDORDER); - Once customer has enter his card data, perform the payment by calling the cardOrder service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK.
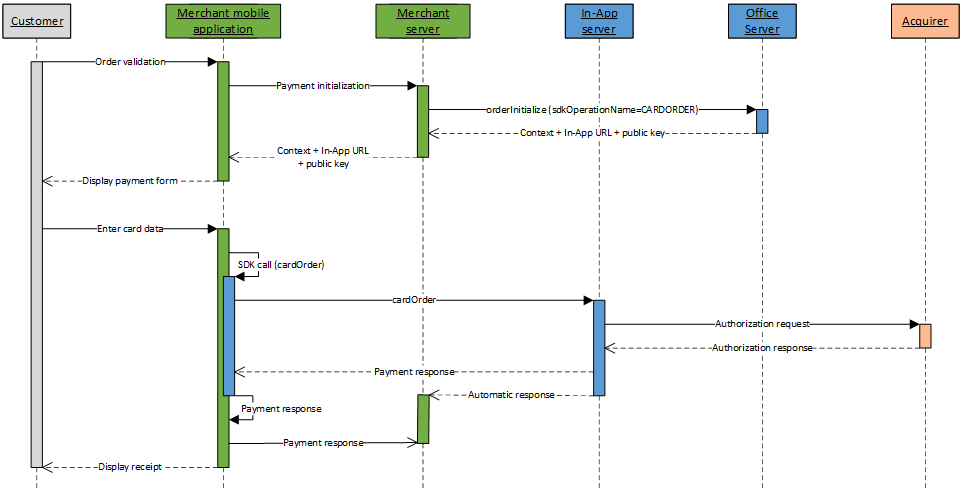
Card payment kinematic with holder authentication
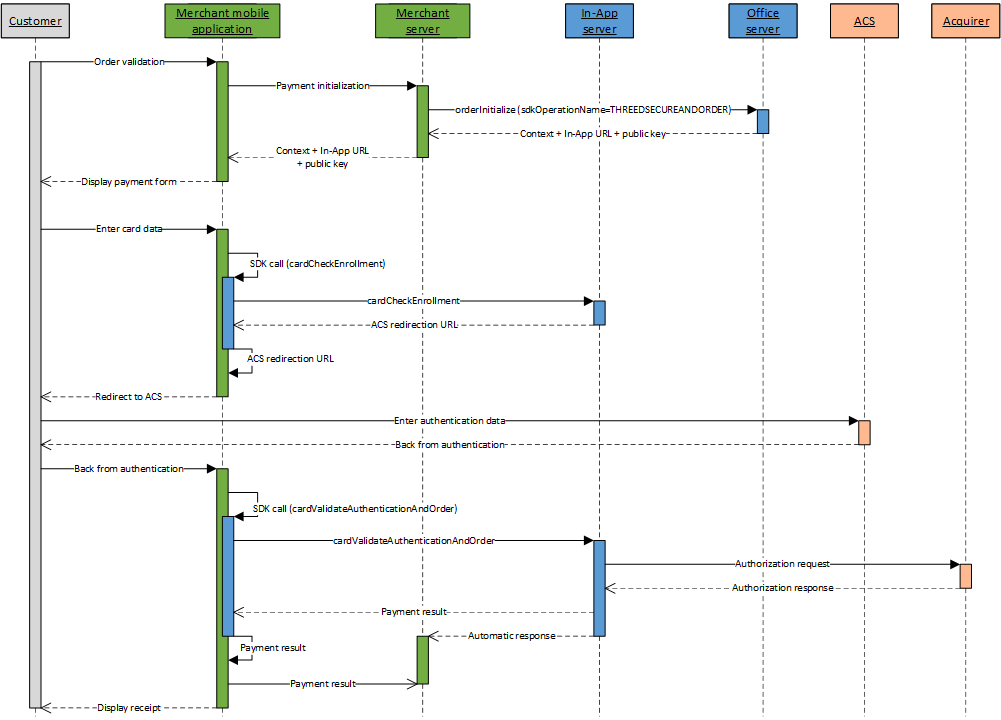
A card payment kinematic with holder authentication with In-App is done in 4 steps:
- Initialize the payment kinematic on Mercanet server
through orderInitialize service (with
sdkOperationName=THREEDSECUREANDORDER); - Once customer has enter his card data, perform a check of the card enrollment by calling the cardCheckEnrollment service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK;
- Redirect the customer to the ACS for authentication;
- Perform the payment by calling the cardValidateAuthenticationAndOrder service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK.
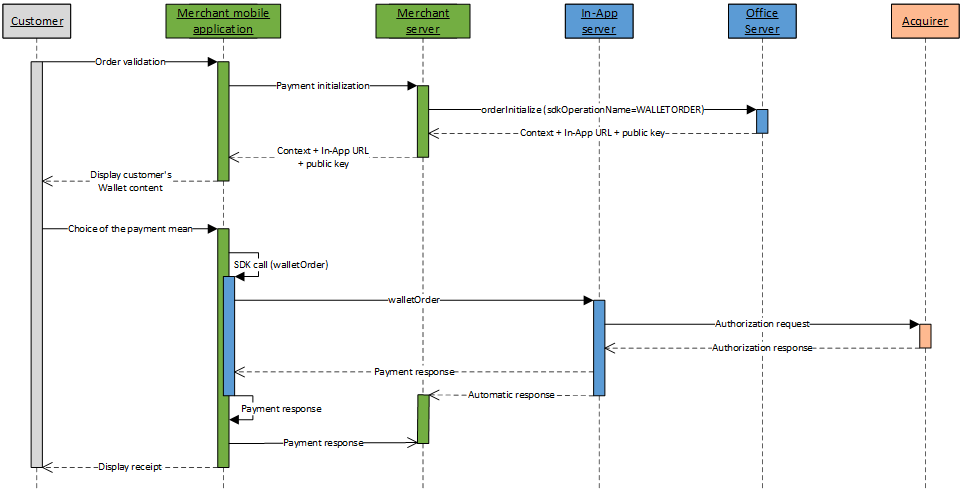
Wallet payment kinematic without holder authentication
A wallet payment kinematic without holder authentication with In-App is done in 2 steps:
- Initialize the payment kinematic on Mercanet server
through orderInitialize service (with
sdkOperationName=WALLETORDER); - Once the customer has chosen his payment mean, perform the payment by calling the walletOrder service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK.
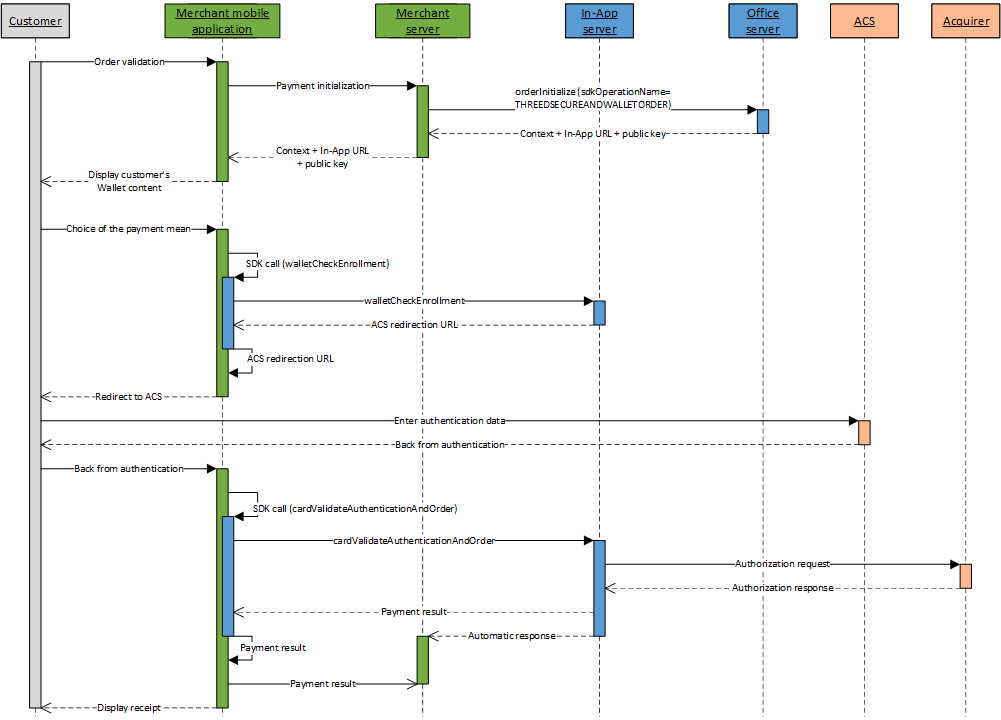
Wallet payment kinematic with holder authentication
A wallet payment kinematic with holder authentication with In-App is done in 4 steps:
- Initialize the payment kinematic on Mercanet server
through orderInitialize service (with
sdkOperationName=THREEDSECUREANDWALLETORDER); - Once the customer has chosen his payment mean, perform a check of the card enrollment by calling the walletCheckEnrollment service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK;
- Redirect the customer to the ACS for authentication;
- Perform the payment by calling the cardValidateAuthenticationAndOrder service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK.
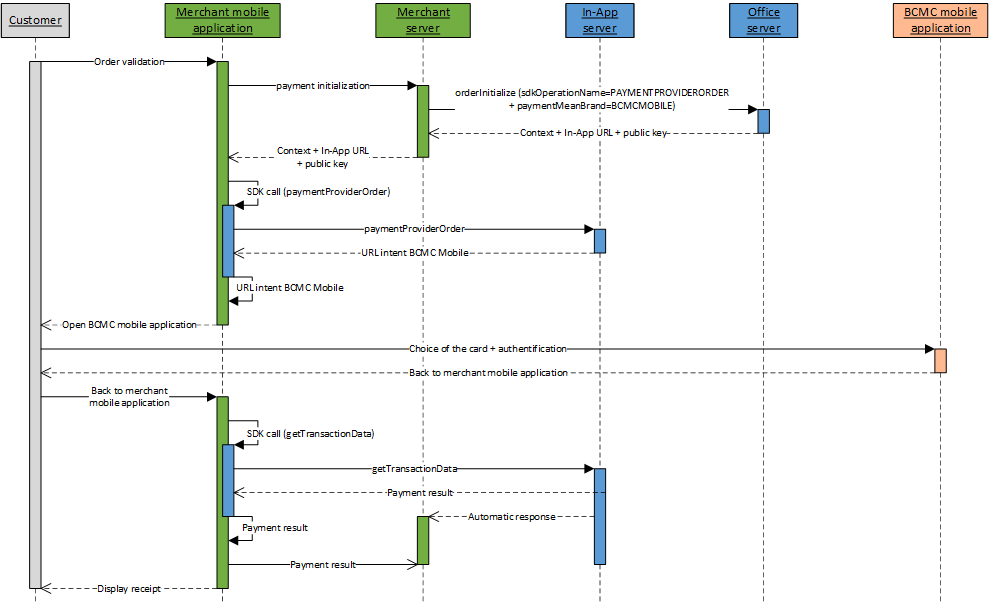
Externalized payment kinematic on a payment provider
An externalized payment kinematic on a payment provider with In-App is done in 4 steps:
- Initialize the payment kinematic on Mercanet server
through orderInitialize service (with
sdkOperationName=PAYMENTPROVIDERORDER); - Perform a call to the paymentProviderOrder service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK, to launch the payment and get the Intent URL which permits to open the payment provider mobile application;
- Redirect the customer to the payment provider mobile application;
- Once the customer is back on the merchant mobile application, perform a call to the getTransactionData service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK, to know the transaction status (payment in success or failure).
Function orderInitialize
The request and response of the function orderInitiliaze are described on this page.
Processing the orderInitialize response
The Mercanet server checks each field received individually. The following list contains the error codes that can be returned during the verification step, as well as the solutions to be implemented.
| redirectionStatusCode | Description |
|---|---|
| 00 | Standard situation followed by the standard call process, from your mobile application, of the wished service (cardOrder, cardCheckEnrollment, walletOrder, walletCheckEnrollment or paymentProviderOrder). |
| 03 | The merchant ID or acquirer contract are not correct. |
| 12 | The transaction parameters are not correct. Check the
request parameters (the error is indicated in the redirectionStatusMessage). |
| 30 | The request format is not correct (the error is indicated
in the redirectionStatusMessage). |
| 34 | Security issue: for example, the calculated seal is not correct. |
| 94 | The transaction already exists. |
| 99 | Service temporarily unavailable. |
4 cases are possible:
redirectionStatusCode= 00
This case must be followed by the call from your mobile application, of the wished service (cardOrder, cardCheckEnrollment, walletOrder, walletCheckEnrollment or paymentProviderOrder).
redirectionStatusCode= 03, 12, 30, 34
These error codes indicate that the request has an issue that must be resolved. The payment process must then be interrupted.
redirectionStatusCode= 94
The transaction reference has already been used. You must try again with another transaction reference.
redirectionStatusCode= 99
Payment service availability issue. You must try to resend the request. A new transaction reference should be used to avoid a 94 response code.
Processing the automatic response at the end of payment kinematic
At the end of the payment kinematic, in addition to the response
returned by Mercanet server to your mobile application
through In-App SDK, you have the possibility to receive
a response directly on your server. This automatic response is a HTTP(S)
POST message sent to the automaticResponseUrl
URL you optionally set in the request.
You must set up the system that will decode this response so you can know the payment result.
The following four data elements are defined in the responses:
| Field name | Comments/rules |
|---|---|
Data |
Fields concatenation in the response |
Encode |
Type of encoding used to encode the Data field |
Seal |
Response message signature |
InterfaceVersion |
Connector interface version |
If the value of the Encode field is "base64" or
"base64url", the Data field should be decoded in
Base64/Base64Url to obtain the concatenated string of fields. The
concatenated string is structured as follows: key1=value1|key2=value2,
etc.
The seal (Seal
field) of both responses is hashed with the same algorithm as the one
supplied as input in the sealAlgorithm
field. If no value was defined, SHA-256 is used by default.
sealAlgorithm
field populated with the value “HMAC-SHA-256”.The value of the Seal
field is computed as follows:
For the HMAC-SHA algorithm:
- use of the shared secret key to generate the HMAC variant of the message;
- use of the
Datafield only (encoded if the corresponding option is selected); - UTF-8 encoding of the data constituting the result of the previous operation;
- HMAC-SHA hashing of the bytes obtained.
This procedure can be summarised as follows:
HMAC-SHA256( UTF-8(Data), UTF-8(secretKey) )For the SHA-256 algorithm (although this is the default value, this algorithm is no longer recommended):
- concatenation of the
Datafield and of the secret key (encoded if the corresponding option is selected); - UTF-8 encoding of the data constituting the result of the previous operation;
- SHA256 hashing of the bytes obtained.
This procedure can be summarised as follows:
SHA256( UTF-8(Data+secretKey) )Providing the automatic response URL
The automatic response is sent only if the automaticResponseUrl
field has been sent in th payment kinematic initialization request. If
this is the case, the Mercanet server sent a HTTP(S) POST
response to the received URL address.
It is your responsibility to retrieve the various data from the response, to check the signature so as to ensure the integrity of the response fields and, consequently, to update your back office.
Choose response format : POST or JSON
From the interfaceVersion HP_3.0 Sips sends you
the concatenated string of the response (Data field) in 2 distinct formats to
choose :
The POST format
This POST format has the following structure : key1=value1|key2=value2…
POST response example with "pipe" separator between the data
captureDay=0|captureMode=AUTHOR_CAPTURE|currencyCode=978|merchantId=039000254447216
|orderChannel=INTERNET|responseCode=00|transactionDateTime=2022-11-14T11:21:12+01:00|transactionReference=SIM20221114112037
|keyVersion=1|acquirerResponseCode=00|amount=1000|authorisationId=664865|guaranteeIndicator=N|panExpiryDate=202401
|paymentMeanBrand=VISA|paymentMeanType=CARD|customerIpAddress=10.78.106.18|maskedPan=############0600|holderAuthentRelegation=N
|holderAuthentStatus=NOT_PARTICIPATING|tokenPan=490700h719850600|transactionOrigin=SIMS|paymentPattern=ONE_SHOT
|customerMobilePhone=null|mandateAuthentMethod=null|mandateUsage=null|transactionActors=null|mandateId=null|captureLimitDate=20221114
|dccStatus=null|dccResponseCode=null|dccAmount=null|dccCurrencyCode=null|dccExchangeRate=null|dccExchangeRateValidity=null
|dccProvider=null|statementReference=null|panEntryMode=MANUAL|walletType=null|holderAuthentMethod=NO_AUTHENT_METHOD
|holderAuthentProgram=3DS_V2|paymentMeanId=null|instalmentNumber=null|instalmentDatesList=null|instalmentTransactionReferencesList=null
|instalmentAmountsList=null|settlementMode=null|mandateCertificationType=null|valueDate=null|creditorId=null
|acquirerResponseIdentifier=null|acquirerResponseMessage=null|paymentMeanTradingName=null|additionalAuthorisationNumber=null
|issuerWalletInformation=null|s10TransactionId=6|s10TransactionIdDate=20221114|preAuthenticationColor=null|preAuthenticationInfo=null
|preAuthenticationProfile=null|preAuthenticationThreshold=null|preAuthenticationValue=null|invoiceReference=null|s10transactionIdsList=null
|cardProductCode=F|cardProductName=VISA CLASSIC|cardProductProfile=C|issuerCode=00000|issuerCountryCode=GRC|acquirerNativeResponseCode=00
|settlementModeComplement=null|preAuthorisationProfile=null|preAuthorisationProfileValue=null
|preAuthorisationRuleResultList=[{"ruleCode":"VI","ruleType":"NG","ruleWeight":"I","ruleSetting":"S","ruleResultIndicator":"0","ruleDetailedInfo":"TRANS=1:3;CUMUL=24999:200000"},{"ruleCode":"RCode","ruleType":"RType","ruleWeight":"RWeight","ruleSetting":"RSetting","ruleResultIndicator":"RIndicator","ruleDetailedInfo":"DetailedInfo"}]
|preAuthenticationProfileValue=null|preAuthenticationRuleResultList=null|paymentMeanBrandSelectionStatus=NOT_APPLICABLE|transactionPlatform=PROD
|avsAddressResponseCode=null|avsPostcodeResponseCode=null|customerCompanyName=null|customerBusinessName=null|customerLegalId=null
|customerPositionOccupied=null|paymentAttemptNumber=1|holderContactEmail=null|installmentIntermediateServiceProviderOperationIdsList=null
|holderAuthentType=null|acquirerContractNumber=3863090010|secureReference=null|authentExemptionReasonList=null
|paymentAccountReference=a667b63d8bec4fb980106497c53e4|schemeTransactionIdentifier=b4e683c1a6ff4a09a0415116a0a25b401d38c19d24e643078d
|guaranteeLimitDateTime=null|paymentMeanDataProvider=null|virtualCardIndicator=N|cardProductUsageLabel=CREDIT|authorisationTypeLabel=TRANSACTION DE PAIEMENT
|authorMessageReference=272612|acceptanceSystemApplicationId=142000000001|challengeMode3DS=null|issuingCountryCode=GRC|abortedProcessingStep=null|abortedProcessingLocation=nullThe JSON format
JSON format has the following structure : { "key1" : "value1", "key2" : "value2", …}
JSON response example
{
"keyVersion": 1, "acquirerResponseCode": "00", "acquirerResponseDescription": "Transaction approved or processed successfully",
"amount": 1000, "authorisationId": "858191", "captureDay": 0, "captureMode": "AUTHOR_CAPTURE", "cardScheme": "VISA",
"chargeAmount": 0, "currencyCode": "978", "customerIpAddress": "10.78.106.18", "guaranteeIndicator": "N",
"holderAuthentRelegation": "N", "holderAuthentStatus": "NOT_PARTICIPATING", "maskedPan": "############0600",
"merchantId": "039000254447216", "orderAmount": 1000, "orderChannel": "INTERNET", "panExpiryDate": "202401",
"paymentMeanBrand": "VISA", "paymentPattern": "ONE_SHOT", "responseCode": "00", "responseDescription": "Process succeeded",
"tokenPan": "490700h719850600", "transactionDateTime": "2022-11-14.11:19:39+0100", "transactionOrigin": "SIMS",
"transactionReference": "SIM20221114111757", "captureLimitDate": "20221114", "paymentMeanType": "CARD", "panEntryMode": "MANUAL",
"holderAuthentMethod": "NO_AUTHENT_METHOD", "holderAuthentProgram": "3DS_V2", "s10TransactionId": "5", "s10TransactionIdDate": "20221114",
"cardProductCode": "F", "cardProductName": "VISA CLASSIC", "cardProductProfile": "C", "issuerCode": "00000", "issuerCountryCode": "GRC",
"acquirerNativeResponseCode": "00", "sealAlgorithm": "sha256", "paymentMeanBrandSelectionStatus": "NOT_APPLICABLE",
"transactionPlatform": "PROD", "paymentAttemptNumber": 1, "acquirerContractNumber": "3863090010",
"schemeTransactionIdentifier": "79e70b862e5942ff86f31951235959a16f45f41f797f48129e",
"paymentAccountReference": "945dbb3e0b984bfc896a04c5bc273", "virtualCardIndicator": "N", "cardProductUsageLabel": "CREDIT",
"authorisationTypeLabel": "TRANSACTION DE PAIEMENT", "authorMessageReference": "179263", "acceptanceSystemApplicationId": "142000000001",
"issuingCountryCode": "GRC", "threeDLiabilityShift": "N", "threeDStatusCode": "NOT_PARTICIPATING", "threeDRelegationCode": "N",
"preAuthorisationRuleResultList":[
{"ruleCode":"VI","ruleType":"NG","ruleWeight":"I","ruleSetting":"S","ruleResultIndicator":"0","ruleDetailedInfo":"TRANS=1:3;CUMUL=24999:200000"},
{"ruleCode":"RCode","ruleType":"RType","ruleWeight":"RWeight","ruleSetting":"RSetting","ruleResultIndicator":"RIndicator","ruleDetailedInfo":"DetailedInfo"}
]
}
Default behaviour since the interfaceVersion HP_3.0
Format of the automatic response is determined by the connector that was used during HTTPS exchanges between your website and Sips servers
| Interface Version | Connector | Response Format |
|---|---|---|
| IR_MB_3.x | JSON | JSON (JS_3.x) |
Choose response versions from the payment request
If you want to override this default behavior it is possible to fill in from the payment request the exact version of the automatic response that you use.
The payment request field which allows to fill in the
automatic response version is interfaceVersionAutomaticResponse
interfaceVersionAutomaticResponse entered in the request is incorrect,
then the payment initialization request fails (error code 30).Solving automatic response reception issues
Below is a list of the most common issues that block the receipt of automatic responses. Please make sure you have checked them before you call the technical support:
- Make sure the automatic response URL is provided in the request and is valid. To do this, simply copy and paste it into the address bar of your browser.
- The supplied URL must be accessible from the outside, i.e the Internet. Access control mechanisms (login/password or IP address filter) or a firewall might block access to your server.
- Access to response URL must be confirmed in the notifications report of your web browser.
- If you use a non-standard port, it must be within the 80 to 9999 range to ensure compatibility with Mercanet.
- Context parameters cannot be added to the response URL. However,
some fields can still be used, e.g the
orderIdorreturnContextfields make it possible to provide extra parameters. You may also use thesessionIdfield to retrieve information about your customer at the end of the payment process.
In some error cases, the Mercanet server is unable to
sign the response message. This applies, for instance, to the "Unknown
merchantId" error and to the situation where the secret key is unknown to
Mercanet. For these particular reasons, the payment server
will send a response without a signature in the Seal
field.
Retrieving the automatic response fields
The content of the response may vary depending on the payment outcome (successful or other), the payment mean and the configuration of your shop.
Automatic response content:
| Field name | As from version | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| acceptanceSystemApplicationId | HP_2.39 | |
| acquirerContractNumber | HP_2.25 | |
| acquirerNativeResponseCode | HP_2.12 | |
| acquirerResponseCode | HP_2.0 | |
| acquirerResponseIdentifier | HP_2.8 | |
| acquirerResponseMessage | HP_2.8 | |
| additionalAuthorisationNumber | HP_2.8 | |
| amount | HP_1.0 | Same as request |
| authentExemptionReasonList | HP_2.28 | |
| authorisationId | HP_1.0 | |
| authorisationTypeLabel | HP_2.39 | |
| authorMessageReference | HP_2.39 | |
| avsAddressResponseCode | HP_2.17 | |
| avsPostcodeResponseCode | HP_2.17 | |
| captureDay | HP_1.0 | Request field which may be overridden by Mercanet. |
| captureLimitDate | HP_2.3 | |
| captureMode | HP_1.0 | Request field which may be overridden by Mercanet. |
| cardCSCResultCode | HP_2.0 | |
| cardProductCode | HP_2.12 | |
| cardProductName | HP_2.12 | |
| cardProductProfile | HP_2.12 | |
| cardProductUsageLabel | HP_2.39 | |
| complementaryCode | HP_1.0 | |
| complementaryInfo | HP_2.0 | |
| creditorId | HP_2.7 | |
| currencyCode | HP_1.0 | Same as request |
| customerBusinessName | HP_2.17 | |
| customerCompanyName | HP_2.17 | |
| customerEmail | HP_2.0 | Same as request |
| customerId | HP_2.0 | Same as request |
| customerIpAddress | HP_2.0 | |
| customerLegalId | HP_2.17 | |
| customerMobilePhone | HP_2.1 | Same as request |
| customerPositionOccupied | HP_2.17 | |
| dccAmount | HP_2.3 | |
| dccCurrencyCode | HP_2.3 | |
| dccExchangeRate | HP_2.3 | |
| dccExchangeRateValidity | HP_2.3 | |
| dccProvider | HP_2.3 | |
| dccStatus | HP_2.3 | |
| dccResponseCode | HP_2.3 | |
| dueDate | HP_2.3 | |
| guaranteeIndicator | HP_2.0 | |
| hashPan1 | HP_2.0 | |
| hashPan2 | HP_2.0 | |
| holderAuthentMethod | HP_2.4 | |
| holderAuthentProgram | HP_2.5 | |
| holderAuthentRelegation | HP_2.0 | |
| holderContactEmail | HP_2.20 | |
| holderAuthentStatus | HP_2.0 | |
| holderAuthentType | HP_2.24 | |
| instalmentAmountsList | HP_2.6 | |
| instalmentDatesList | HP_2.6 | |
| instalmentNumber | HP_2.6 | |
| instalmentTransactionReferencesList | HP_2.6 | |
| interfaceVersion | HP_1.0 | |
| intermediateServiceProviderOperationId | HP_2.23 | |
| invoiceReference | HP_2.10 | |
| issuerCode | HP_2.12 | |
| issuerCountryCode | HP_2.12 | |
| issuerEnrollementIndicator | HP_2.0 | |
| issuerWalletInformation | HP_2.9 | |
| issuingCountryCode | HP_2.44 | |
| keyVersion | HP_1.0 | Same as request |
| mandateAuthentMethod | HP_2.2 | |
| mandateCertificationType | HP_2.7 | |
| mandateId | HP_2.3 | |
| mandateUsage | HP_2.2 | |
| maskedPan | HP_1.0 | |
| merchantId | HP_1.0 | Same as request |
| merchantSessionId | HP_2.0 | Same as request |
| merchantTransactionDateTime | HP_2.0 | Same as request |
| merchantWalletId | HP_2.0 | Same as request |
| orderChannel | HP_2.0 | Same as request |
| orderId | HP_1.0 | Same as request |
| panEntryMode | HP_2.4 | |
| panExpiryDate | HP_2.0 | |
| paymentAccountReference | HP_2.28 | |
| paymentAttemptNumber | HP_2.18 | |
| paymentMeanBrand | HP_1.0 | |
| paymentMeanBrandSelectionStatus | HP_2.14 | |
| paymentMeanData | HP_2.2 | |
| paymentMeanId | HP_2.6 | |
| paymentMeanTradingName | HP_2.8 | |
| paymentMeanType | HP_1.0 | |
| paymentPattern | HP_2.0 | Same as request |
| preAuthenticationColor | HP_2.10 | |
| preAuthenticationInfo | HP_2.10 | |
| preAuthenticationProfile | HP_2.10 | |
| preAuthenticationProfileValue | HP_2.14 | |
| preAuthenticationRuleResultList | HP_2.14 | List of ruleResult objects. Please see below for its content and format. |
| preAuthenticationThreshold | HP_2.10 | |
| preAuthenticationValue | HP_2.10 | |
| preAuthorisationProfile | HP_2.14 | |
| preAuthorisationProfileValue | HP_2.14 | |
| preAuthorisationRuleResultList | HP_2.14 | List of ruleResult objects. Please see below for its content and format. |
| responseCode | HP_1.0 | |
| returnContext | HP_1.0 | Same as request |
| s10TransactionId | HP_2.9 | |
| s10TransactionIdDate | HP_2.9 | |
| s10transactionIdsList | HP_2.11 | |
| schemeTransactionIdentifier | HP_2.28 | |
| scoreColor | HP_2.0 | |
| scoreInfo | HP_2.0 | |
| scoreProfile | HP_2.0 | |
| scoreThreshold | HP_2.0 | |
| scoreValue | HP_2.0 | |
| secureReference | HP_2.26 | |
| settlementMode | HP_2.7 | |
| settlementModeComplement | HP_2.13 | |
| statementReference | HP_2.4 | |
| tokenPan | HP_2.0 | |
| transactionActors | HP_2.2 | Same as request |
| transactionDateTime | HP_1.0 | |
| transactionOrigin | HP_2.0 | Same as request |
| transactionPlatform | HP_2.16 | For future use (for now, its value is systematically set to ‘PROD’). |
| transactionReference | HP_1.0 | |
| virtualCardIndicator | HP_2.36 | |
| walletType | HP_2.4 |
ruleResult content:
| Field name | As of version | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| ruleCode | HP_2.14 | |
| ruleType | HP_2.14 | |
| ruleWeight | HP_2.14 | |
| ruleSetting | HP_2.14 | |
| ruleResultIndicator | HP_2.14 | |
| ruleDetailedInfo | HP_2.14 |
The syntax of a complex objects list in the automatic response is defined as follow:
...|amount=1000|currencyCode=978|objectNameList=[{"field1":"value1a",
"field2":"value2a","field3":"value3a"…},{"field1":"value1b",
"field2":"value2b","field3":"value3b"}…]|transactionReference=1452687287828|...- The content of the list is in square brackets [ ];
- Each entry of the list is in curly brackets { };
- Each field is represented as "fieldName" = "fieldValue";
- Please note that the name and the value of the field are both in double quotes "";
- Pairs of adjacent names/values are separated by a comma.
Sample with the preAuthorisationRuleResultList
field:
...|amount=1000|currencyCode=978|preAuthorisationRuleResultList=[
{”ruleCode”:"SC",”ruleType”:"NG",”ruleWeight”:"I",”ruleSetting”:"S",
”ruleResultIndicator”:"0",“ruleDetailedInfo”:"TRANS=1:5;
CUMUL=1000:99999900"},{”ruleCode”:"GC",”ruleType”:"NG",”ruleWeight”:
"D",”ruleSetting”:"N",”ruleResultIndicator”:"0",“ruleDetailedInfo”:
""},{”ruleCode”:"CR",”ruleType”:"NG",”ruleWeight”:"D",”ruleSetting”
:"S",”ruleResultIndicator”:"N",“ruleDetailedInfo”:"CARD_COUNTRY=USA"}]
|transactionReference=1452687287828|...Analysing the payment response
Once the payment kinematic ended, you must analyse the response to know the payment result. This response is furnished to your mobile application in return of the payment function called, as well as to the automatic response URL if you filled it in the initialization request.
If you carry out the authentication steps by means of an electronic seal, you should make sure the seal you received actually matches the seal you recomputed using the response fields.
| Status | Response fields | Actions to be carried out |
|---|---|---|
| Payment accepted | responseCode
= 00acquirerResponseCode
= 00guaranteeIndicator
= Y, N, U, empty |
You can deliver the order according to the guarantee level
of your choosing (guaranteeIndicator
field). |
Mercanet fraud
refusal Go-No-Go |
responseCode
= 05complementaryCode
= XXpreAuthorisationRuleResultList |
The payment has been refused by the Mercanet fraud engine that you configured. Do not
deliver the goods. Analyse in detail the fraud rules
executed by Mercanet to know the reason for the
refusal ( preAuthorisationRuleResultList
field). |
Mercanet fraud
refusal Business Score |
responseCode
= 05scoreColor
= RED, BLACKscoreValue
= X (transaction score)scoreThreshold
= X,Y (orange threshold, green threshold) |
The payment has been refused by the Mercanet fraud engine that you configured. Do not
deliver the goods. Analyse in detail the fraud rules
executed by Mercanet to know the reason for the
refusal ( preAuthorisationRuleResultList
field). |
Mercanet fraud
warning Business Score |
responseCode
= 05scoreColor
= ORANGEscoreValue
= X (transaction score)scoreThreshold
= X,Y (orange threshold, green threshold) |
The acquirer has authorised the payment, but the
Mercanet fraud engine issued a warning due to the
rules you configured. Analyse in detail the fraud rules
executed by Mercanet to know the reason for the
warning ( preAuthorisationRuleResultList
field).
The acceptChallenge and refuseChallenge
functions are available on the extranet and the Office (M2M) connectors. |
| 3-D Secure refusal | responseCode
= 05holderAuthenStatus
= FAILURE |
Customer authentication failed. This is not
necessarily due to fraud. You can suggest to your
customer to attempt the payment again with another means of
payment, by generating a new request. |
| Banking refusal from the acquirer | responseCode
= 05acquirerResponseCode
= XX |
Authorisation refused for a reason not related to
fraud. You can suggest to your customer to attempt the
payment again with another means of payment, by generating a new
request. |
| Soft decline | responseCode
= 05acquirerResponseCode
= A1 |
The payment has been refused by the acquirer because
the 3-D Secure data is missing in the authorisation
request. Please try to pay again with a 3-D Secure
payment process. |
| Fraud refusal from the acquirer | responseCode
= 34acquirerResponseCode
= XX |
Authorisation refused because of fraud. Do
not deliver the order. |
| Refusal due to a technical issue | responseCode
= 90, 99acquirerResponseCode
= 90 to 98 |
Temporary technical issue while processing the
transaction. Please tell your customer to attempt the
payment again later. |
Initializing a wallet management kinematic
With In-App connector, you are able to launch
several kind of wallet management kinematic according to sdkOperationName
field, filled in walletInitialize service request:
- Kinematic to consult a customer's wallet content (
sdkOperationName=GETWALLETDATA) - Kinematic to add a card to a customer's wallet (
sdkOperationName=ADDCARD) - Kinematic to delete a payment mean from a customer's wallet (
sdkOperationName=DELETEPAYMENTMEAN)
These kinematics are described hereafter.
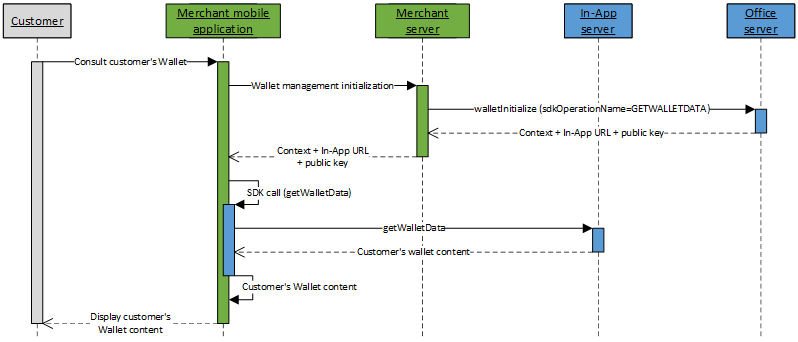
Wallet consultation kinematic
The kinematic to consult customer's Wallet with In-App is done in 2 steps:
- Initialize the Wallet management kinematic on Mercanet server through walletInitialize service (with
sdkOperationName=GETWALLETDATA); - Perform a call to getWalletData service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK.
Once the content of customer's Wallet collected, you can display it the your customer for him to manipulate it (add or delete a payment mean in the Wallet) or perform a payment from a registered card.
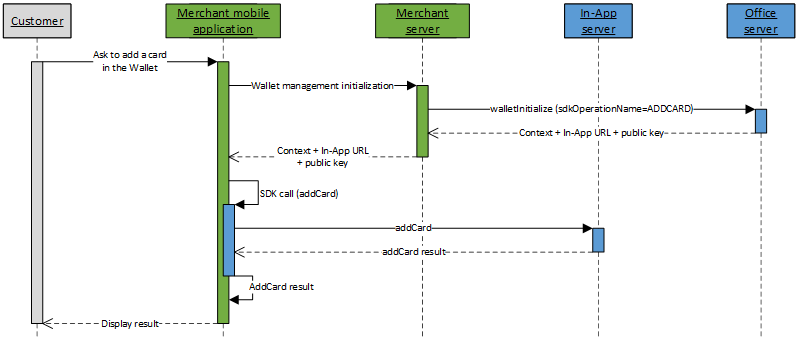
Add a card to the Wallet kinematic
The kinematic to add a card to customer's Wallet with In-App is done in 2 steps:
- Initialize the Wallet management kinematic on Mercanet server through walletInitialize service (with
sdkOperationName=ADDCARD); - Perform a call to addCard service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK.
Delete a payment mean from the Wallet kinematic
The kinematic to delete a payment mean from a customer's Wallet with via In-App is done in 2 steps:
- Initialize the Wallet management kinematic on Mercanet server through walletInitialize service (with
sdkOperationName=DELETEPAYMENTMEAN); - Perform a call to deletePaymentMean service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK.
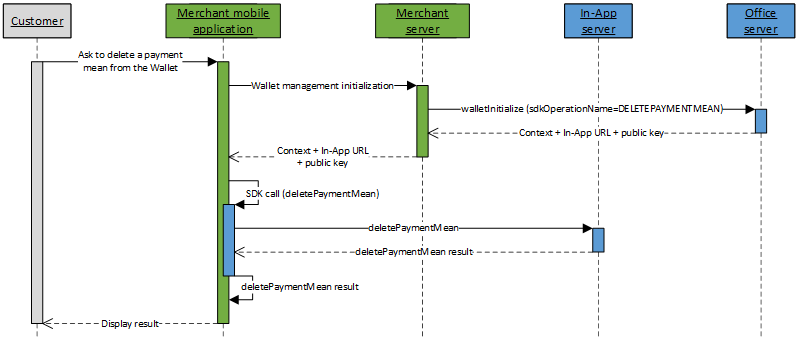
Function walletInitialize
The request and response of the function walletInitiliaze are described on this page.
Processing the walletInitialize response
The request and response of the function walletInitiliaze are described on this page.
Analysing the wallet management response
Once the wallet management kinematic ended, you must analyse the response to know the processing result. This response is furnished to your mobile application in return of the wallet management function called.
| Status | Response fields | Action to be carried out |
|---|---|---|
| Wallet management operation taken into account | walletLastActionDateTime
populated with the date/time of the last action carried out on the
wallet.walletPaymentMeanDataList
contains the payment methods in the wallet
after-update. |
To avoid requesting the card information on the next
payment with the function getWalletData, store the following
wallet data in your customer database:
|
| Wallet management operation not taken into account | walletLastActionDateTime
not populated with current date/time.walletPaymentMeanDataList
contains the payment methods in the wallet. |
If the wallet update is required then submit a request again |
Initializing a card data consultation kinematic
With In-App connector, you are able to launch a
kinematic to consult data linked to the card of a customer with
paymentMeanInfoInitialize service, with the field sdkOperationName
valued to GETCARDDATA.
You may use this kinematic to get a customer card brands and propose him to choose the brand to use for the payment (for more information about regulatory "brand selection", you can consult the brand selection guide).
Get card data kinematic
The kinematic to consult card data with In-App is done in 2 steps:
- Initialize the kinematic to consult card data on Mercanet server through paymentMeanInfoInitialize service
(with
sdkOperationName=GETCARDDATA); - Once the card number is entered by the customer, perform a call to getCardData service from your mobile application, thanks to the In-App SDK.
Once properties of the card are known, you are able to, for example, to display to the card holder the brands of the card, and propose him to choose his preferred brand to perform the payment.
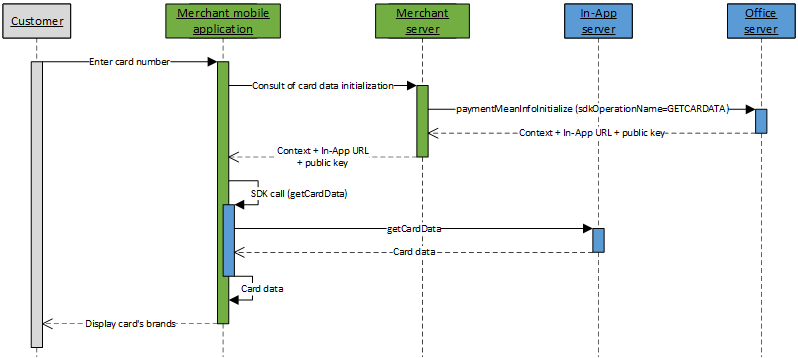
Function paymentMeanInfoInitialize
The request and response of the function paymentMeanInfoInitiliaze are described on this page.
Processing the paymentMeanInfoInitialize response
The Mercanet server checks each field received individually. The following list contains the error codes that can be returned during the verification step, as well as the solutions to be implemented.
| redirectionStatusCode | Description |
|---|---|
| 00 | Standard situation followed by the standard call process, from your mobile application, of the getCardData service. |
| 03 | The merchant ID or acquirer contract are not correct. |
| 12 | The transaction parameters are not correct. Check the
request parameters (the error is indicated in the redirectionStatusMessage). |
| 30 | The request format is not correct (the error is indicated
in the redirectionStatusMessage). |
| 34 | Security issue: for example, the calculated seal is not correct. |
| 40 | Unauthorised function. |
| 99 | Service temporarily unavailable. |
3 cases are possible:
redirectionStatusCode= 00
This case must be followed by the call from your mobile application, of the getCardData service.
redirectionStatusCode= 03, 12, 30, 34, 40
These error codes indicate that the request has an issue that must be resolved. The payment process must then be interrupted.
redirectionStatusCode= 99
Payment service availability issue. You must try to resend the request.
Step 3: Implementing the SDK
This step may be done in parallel with step 2. It consists in implementing interactions between your mobile application and the services proposed in In-App SDK, depending on the kinematics you wish to implement.
Step 4: testing in the customer's test environment
The test and integration steps can be implemented using the test environment.
The URL for the test environment is: https://office-server-mercanet.test.sips-services.com
| Payment initialization service | /rs-services/v2/checkoutInApp/orderInitialize |
| Wallet management initialization service | /rs-services/v2/walletInApp/walletInitialize |
| Card data consultation initialization service | /rs-services/v2/paymentMeanInfoInApp/paymentMeanInfoInitialize |
| Merchant ID | 201040027570001 |
| Key version | 1 |
| Secret key | H6znJWqPj9cTRFe9eT62ulurkb_Lrksbw4PFtMSVb74 |
The authorisation process is simulated in the customer's test environment. This means you do not need to use real payment methods to carry out tests.
You can use the following data for your tests:
| Tests cards | cf page "Test cards" |
| Security code | 123 |
| Validity date | must be greater than the current month |
transactionReference.
Therefore, you must set the transactionReference
field in your test requests.merchantId
is shared by all merchants and prospects, there might be transactionReference
duplicates. This is why it is highly recommended to prefix all transactionReferences
with the name of the future shop that will be used in the production
environment. This also makes support easier if you call the technical
support.Step 5: validating the switch to the production environment
Once you have tested the connection from your mobile application to In-App, you can validate the connection to the production version of In-App.
Prior to this, we recommend you block public access to your mobile application to prevent customers from carrying out transactions during this validation phase.
To switch to the production server, you must change the URL in order to connect to the Mercanet production server using the merchantId, secretKey and keyVersion credentials you received during the registration phase.
| URL | https://office-server.mercanet.bnpparibas.net |
| merchantId | Shop identifier received by e-mail |
| secretKey | Secret key you can retrieve from the Mercanet Téléchargement extranet |
| keyVersion | Secret key version retrieved from Mercanet Téléchargement (obviously 1 for the first key) |
How to validate the proper functioning in the production environment
Immediately:
- Make a transaction using a real payment card (your own, if possible). If the transaction is accepted, it will be sent to the bank to credit your merchant account and to debit the card account.
- Check the transaction via Mercanet Back Office, using the
transactionReference
The next day:
- Make sure the transaction is in the Transactions report.
- Check your account to make sure the operation was credited.
- Refund the transaction via Mercanet Back Office (optional).
Two days later:
- Check that the refund transaction is in the Operations report.
- Make sure the debited amount has been refunded to your merchant account.
Step 6: launching live operation
Once the validation for the transition to live operation has been carried out, make your site public so your customers can make purchases and payments.
On the same day:
- Monitor acceptance rates (number of
responseCode00 per total number of transactions). - Check the nature of non-banking refusals:
- Technical issue:
responseCode90, 97, 99 - Fraud:
responseCode34 - Max number of payment attempts reached:
responseCode75
- Technical issue:
The next day:
- Check that all transactions processed (accepted and refused) are in the Transactions report.
- Check the operations you have carried out and remittances (report option) in the Operations report.